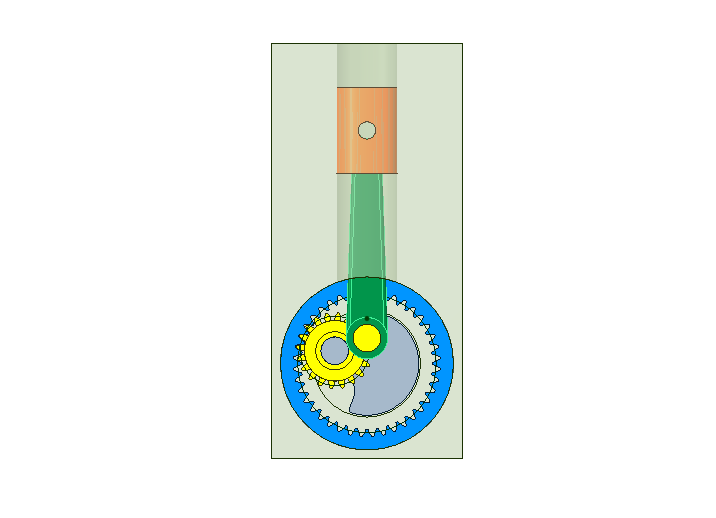
In this tutorial, we import a Vertical Engine (Concept) assembly from GrabCAD. The beauty of this concept is that the connecting rod always remains vertical and the crank is in the form an internal gear.
In the video tutorial below:
- We have imported assembly from GrabCAD inside SpaceClaim.
- Define assembly conditions between different components
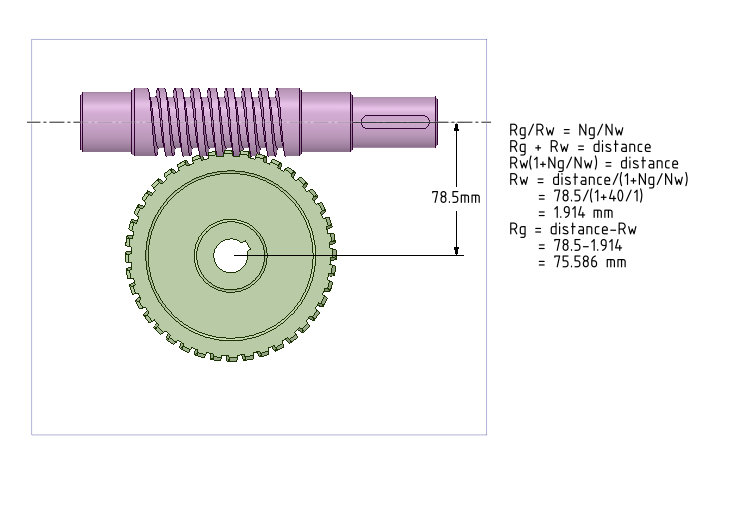
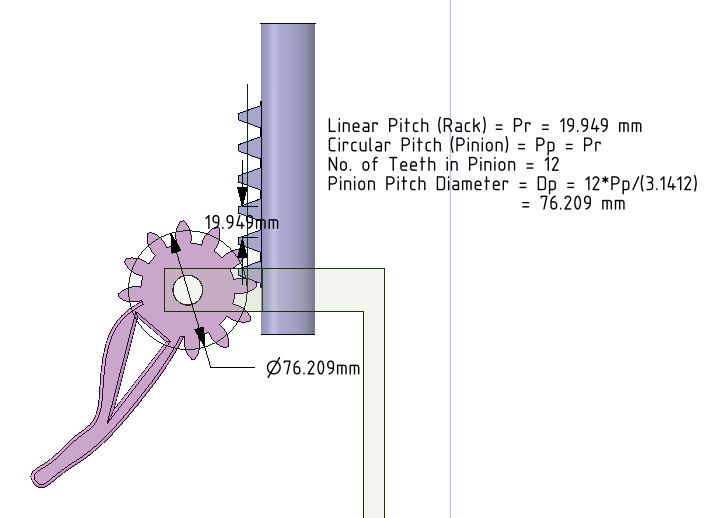
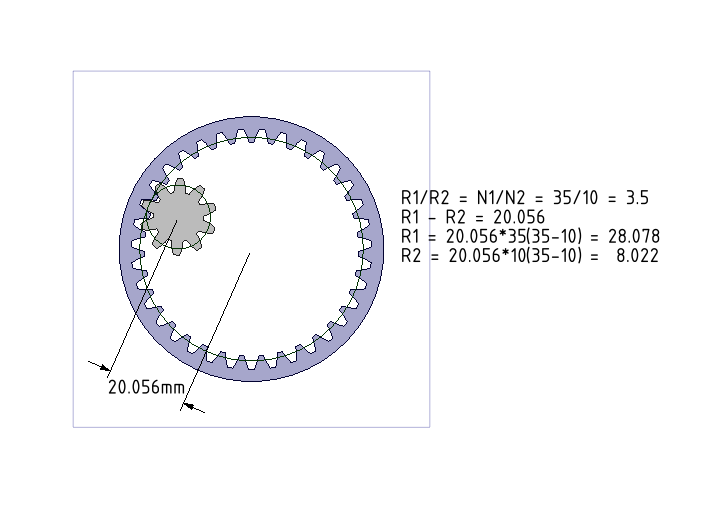
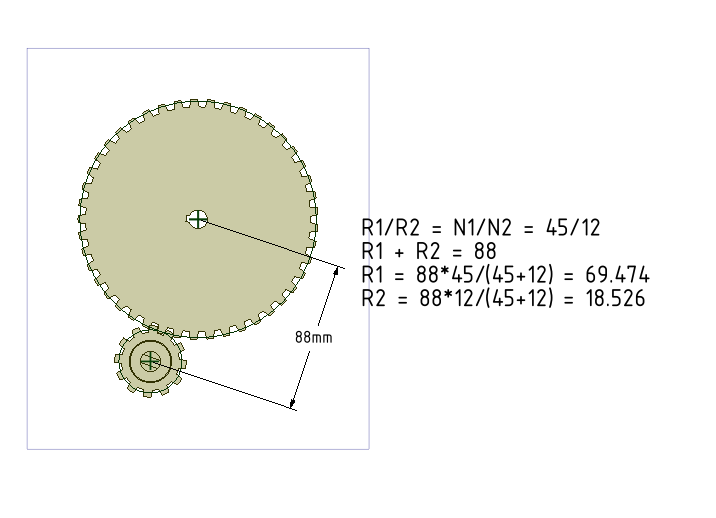
- Draw pitch cylinders for Internal Gears. More details can be seen at our earlier tutorial.
- We have just defined a Gear condition between the pitch cylinders and the gear meshing is perfect. In general, we should also assign a Tangent condition between the same two pitch cylinders (surfaces).
- We observe that the cylindrical hole for the piston to go up and down is not at the right place. We move this hole very easily inside SpaceClaim to its right place.
- Move the crank and see the piston go up and down.
- Start SC-Motion and simulate the motion by defining rotation at the crank.
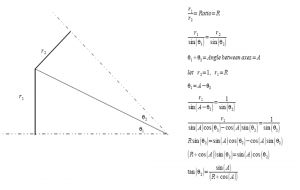
If you place a gear inside another gear, with the internal gear having a tooth count of half the ring gear’s tooth count, any point on the pitch diameter of the inside gear will move back and forth in a straight line.